Exploring the Red Planet: An Introduction To Mars
Have you ever wondered what lies beyond the red planet? For thousands of years, humans have been fascinated by Mars, speculating about its mysteries and dreaming of one day visiting this distant world. From its impressive mountains to its deep craters, from its vast deserts to its eerie atmosphere—Mars is a planet that has captivated minds for generations. In this article, we will explore all there is to know about the Red Planet; a journey through space and time where ancient secrets await us. So join us as we take an exciting voyage into discovering what makes Mars such an intriguing place!
I. The History of Mars Exploration
The exploration of Mars has been a captivating topic for many centuries. It began with ancient astronomers and philosophers speculating about the mysterious red planet, followed by scientists designing ways to send humans into space and land on its surface. But it wasn’t until the 1960s that these dreams became reality.
In 1964, NASA launched Mariner 4 on an unmanned mission to flyby Mars and take pictures of its surface. On July 15th 1965, the spacecraft flew within 6100 kilometers (3,800 mi) of Mars’ surface and transmitted 22 photographs back to Earth – marking the first time humanity had ever seen what another planet looked like up close. This was just the beginning of our journey into space exploration; over the following decades we sent more probes deeper into outer space in search of knowledge about our solar system’s planets and moons.
Throughout history there have been numerous robotic missions exploring both Martian orbiters as well as rovers on its surface. One example is NASA’s Curiosity rover which landed in 2012 with a goal to determine if Mars ever had conditions suitable for life-forms existing thereon or not. This rover still continues to explore mars today! In addition, there are also plans for human missions in coming years; by 2024 Elon Musk hopes his company SpaceX will be able to launch astronauts aboard their Starship rocket towards the red planet!
These explorations have enabled us to learn more than ever before about this distant world: from discovering evidence water once flowed freely across its terrain, uncovering signs that tiny microbial organisms may have once lived beneath its ground layers – all while turning myths into facts along this incredible journey through time & science!
II. Facts About the Planet’s Geography and Landscape
Earth is a beautiful and complex planet, not just in terms of its stunning beauty but also due to the intricate geographical features it contains. From the highest mountains on land to the deepest trenches in our ocean floors, Earth has many remarkable features that make it unique from other planets.
Mountains
- The tallest mountain range on Earth is found in Asia and is known as The Himalayas. It spans across five countries: India, Nepal, Bhutan, China, and Pakistan.
- The highest peak within this range is Mount Everest which stands at 892 meters tall.
- Another famous mountain range located on Earth is The Alps. This range stretches through eight different European countries such as Austria and Germany.
Seas & Oceans
- Earth has five oceans including Pacific Ocean , Atlantic Ocean , Indian Ocean , Arctic Ocean & Southern
Ocean . - Some of the largest seas located within these oceans include the South China Sea, Caribbean Sea & Mediterranean Sea
The Martian Atmosphere and Climate
Atmospheric Composition: The atmosphere of Mars is composed mostly of carbon dioxide (95.32%) with a few other trace gases like argon, oxygen and nitrogen making up the remaining 4.68%. Despite this high level of CO2, Martian air is incredibly thin in comparison to Earth’s atmosphere – averaging just 0.6% of the pressure found at sea level on our planet! This makes it difficult for humans to breathe and visit without specialized equipment or protection from extreme temperatures.
Climate: While Mars does have seasons much like Earth does, they are caused by slightly different phenomena than those experienced here on our home planet. On Mars, most notably during the summer months when temperatures reach their highest levels, strong winds blow dust particles around creating huge storms that can last up to weeks at a time! These storms can obscure visibility and even block out sunlight if they become particularly powerful enough – making them an unwelcome surprise for any visitors hoping to explore the red planet’s surface.
Temperature Extremes: Temperatures across Mars vary greatly depending on location and season – ranging from a low average temperature of about −153 °C (−243 °F) near its poles in wintertime all the way up to 27 °C (80 °F) near its equator during summertime! Such extremes make life difficult not only for human explorers but also anything else trying survive there as well; though some microbes have been found living in extremely hostile conditions on other worlds such as those within Antarctica’s Dry Valleys – so who knows what might be lurking beneath Martian soil?
IV. What Lies Beneath the Surface of Mars?
Mars has always been a source of mystery and fascination for human beings on Earth. It is the closest planet to our own, yet it remains largely unexplored due to its inhospitable environment. What lies beneath the Mars surface? Scientists are beginning to uncover clues that may help us better understand this enigmatic world.
For starters, Mars features an atmosphere filled with carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxide, argon, and traces of other gases such as water vapor and methane. As we have seen in recent missions sent by NASA, there also appears to be evidence of subsurface water ice located near the poles. This ice could potentially provide resources for future exploration or colonization efforts on Mars.
On top of that, scientists believe that there is a vast reservoir of magma underneath the Martian surface – similar to what exists beneath Earth’s continents today – which could explain why some regions appear much more rugged than others when viewed from orbit. Plus, seismic data collected from previous landers indicates that certain parts of the planet may contain significant amounts of mineral deposits like iron ore or copper ore – something which would be immensely valuable if it were ever accessible enough for humans to mine in person one day!
V. Searching for Life on Mars – Past, Present, and Future Missions
The search for life on Mars has captivated scientists and curious minds alike since the dawn of time. The red planet is shrouded in mystery, prompting humans to explore its secrets in hopes of discovering the answer to one of the universe’s greatest questions: Is there life beyond Earth?
Past Missions
In 1965,NASA launched Mariner 4, a robotic mission that sent back 22 photographs from Mars. These images showed that much like our own moon, Mars was an arid desert with vast areas of craters and canyons. Later flybys further revealed evidence of volcanoes and riverbeds indicating possible water-filled lakes or oceans in Mars’ past.
Present Missions
Today’s missions are far more sophisticated than those before them. NASA’s Curiosity rover has been exploring Gale crater since 2012 while InSight detected quakes beneath the surface using seismic instruments last year. Meanwhile, other rovers such as Opportunity have located rock formations indicative of former salty seas by analyzing minerals within their composition.
- These instruments also measure air pressure, temperature, wind speed and direction.
Future Missions
With each new discovery comes further proof that at one point during its historyMars may have had habitable conditions – bolstering hope for potential alien life forms on the red planet today! So what do we have planned for future exploration? Well upcoming missions will seek to answer this very question through a combination aerial imaging satellites combined with landers equipped with advanced scientific tools capable measuring everything from atmospheric particles to underground radiation levels.
This data will be crucial when it comes to understanding if anything living still exists on mars.
VI. Why We Should Continue to Explore Our Neighbor in Space
A Historical Perspective
Since the dawn of humanity, we have been fascinated by our neighbor in space – the Moon. Early civilizations dreamed of one day being able to visit it and explore its mysterious surface. Through countless generations, advances in science and technology have brought us closer to realizing those dreams. From our first footsteps on the lunar surface with Apollo 11, to robotic rovers sent out more recently, each mission has given us greater insight into what lies beyond Earth’s atmosphere.
New Discoveries Await
We now know there is much left to be discovered on the Moon and our exploration should continue as far as possible! For example, recent findings suggest that water may exist beneath its icy crust which could potentially provide a valuable source for future human missions. On top of that, many scientists speculate that asteroids from long ago may be trapped inside craters near the poles – this would offer a unique opportunity for study never before seen in history! Finally, studies about seismic activity could give us invaluable data about how planets form over time and help answer fundamental questions about our own origins.
The Benefits Speak For Themselves
Along With furthering scientific knowledge, exploring deeper into space also brings other benefits such as developing new technologies here on Earth. Our current research projects require advanced designs for spacecrafts capable of surviving extreme conditions while still providing accurate readings; these same innovations can then be applied elsewhere – leading towards better transportation systems or improved medical treatments just to name a few possibilities! Overall it’s clear that delving even further into what lies beyond will not only uncover secrets hidden away since creation but also bring tangible results right back home where they are most needed – making sure no effort goes wasted along the journey of discovery!
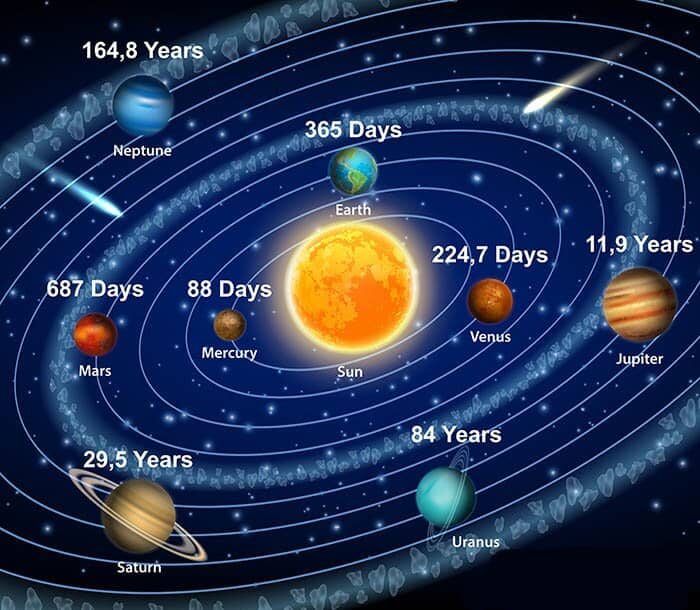
VII. Exploring Beyond: Taking a Look at Other Planets in our Solar System
The Adventure Awaits!
Exploring beyond the boundaries of Earth has been a longstanding dream for mankind. Since the dawn of time, we have looked up to the stars in wonder and awe, dreaming of what lies beyond our own planet. With recent advancements in technology and space exploration, this dream has become more attainable than ever before. In modern times, we have seen humanity step out into the void and make great strides towards understanding our Solar System better than ever before; from unmanned probes that take detailed images of distant planets to manned missions that allow humans to experience another world first-hand.
While much attention is paid to exploring Mars due its potential habitability for human life, there are many more exciting destinations within our Solar System waiting to be explored. From mysterious moons orbiting Saturn (like Enceladus which may contain a liquid ocean beneath its icy surface) or Jupiter’s volcanic moon Io with over 400 active volcanoes on it’s surface – these places offer a wide range of possibilities worth investigating further. Another fascinating find was made by Voyager 1 when it flew past Uranus in 1986 – discovering ten new moons that had gone previously undetected!
The Solar System holds many secrets yet uncovered by mankind and offers us an incredible opportunity for scientific discovery as well as personal exploration. By studying other planets in detail through remote sensing techniques such as radar imaging or spectroscopy, scientists can gain valuable insight about their composition and atmosphere which can help inform future manned missions or even colonization efforts if possible one day! On top of that, visiting these exotic worlds offers us an entirely unique perspective on our place within existence – allowing us glimpse at what could be awaiting us if only we go out there and explore!