19 Star Facts: Stellar Classifications Explained & More!
If you’re looking to learn some more about stars, then you’re in luck. The stars in our sky are often misunderstood by humans, as many people think that they’re in the same solar system as our planet, Sun and the Moon. Well, they’re not, except one giant star that happens to be the center of our solar system.. the Sun! Let’s get started with some interesting star facts.
Star Facts
- There are an estimated minimum of 100 thousand million stars in our Milky Way.
- Of course, this is just in our galaxy, the Milky Way. There are billions more galaxies out there, and trillions more stars.
- Stars are primarily made up of Hydrogen and Helium. This is the sane as the planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune.
- Of course, this is the same as the Sun, which is also a star! This is the only star in our solar system.
- Although it feels like there might be millions of stars visible in the sky, this isn’t actually true. There are only a few thousand, between 5,000 and 9,000, visible in the night sky to the naked eye.
- The hottest stars in the night sky are blue, whilst the coolest stars in the sky are red.
- Red dwarf stars make up around 65-70% of all the stars in our universe. That means that around 2 in every 3 stars are red dwarfs, which are a type of main sequence star.
- The stars are put into different classifications, ranging from a white dwarf star all the way up to a hypergiant star.
- Our Sun is a dwarf star, meaning there are many stars bigger than it out there in the Universe.
- Each star goes through its own life cycle. The length of this life cycle is dependent on its mass.
The 5 Brightest Stars
When we’re looking into the sky, there are some stars that shine brighter than others. Here’s a list of the five brightest stars in our universe as they appear from Earth.

Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in our night sky. It is part of the Canis Major constellation.

Canopus
After Sirius, Canopus is the next brightest star. It’s part of the constellation Carina, which is best seen from the Southern hemisphere.

Alpha Centauri
Alpha Centauri is the closest star system to our own. It is part of the Centaurus constellation.

Arcturus
Arcturus is the fourth brightest star, and it’s part of the Bootes constellation. It is a red giant star.

Vega
Vega is only 25 light years from Earth. It makes up the constellation Lyra.
Star Sizes
Whilst these are the brightest stars, it doesn’t mean they’re the biggest. In fact, there are stars that are much bigger than these stars that just aren’t as bright.
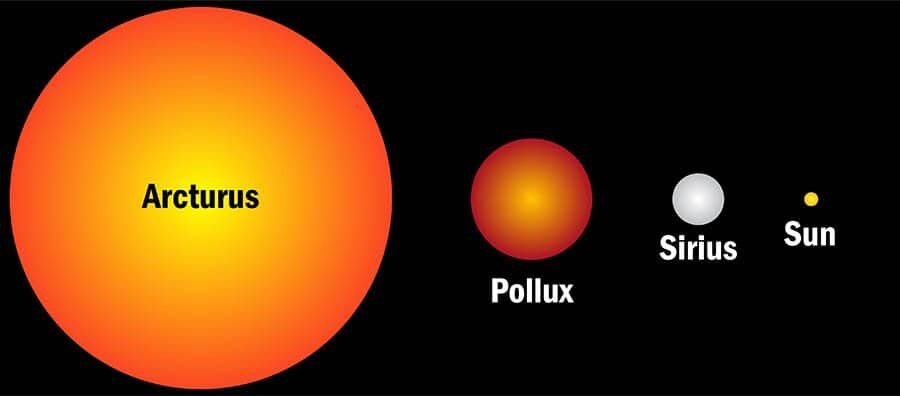
This image show how big Arcturus is compared to not only Sirius, a star which is brighter, but also in comparison to the Sun.
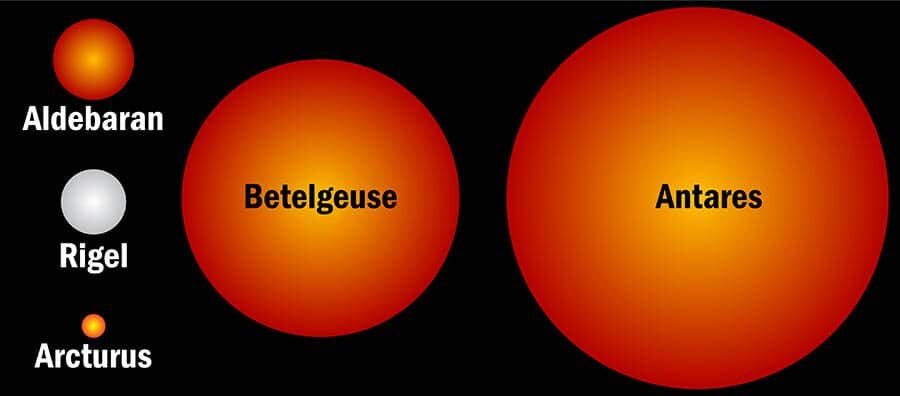
And again, this image compares the size of Arcturus to the size of Antares. So, you can imagine the massive different between the Sun and Antares!
Stellar Classifications of Stars
When we are classifying stars into different categories, we do this via two different methods. The first method is the Harvard method; this is done by using the stars surface temperature. The second method is known as the MK method, which we classify stars based on their luminosity. It can get a little confusing sometimes!
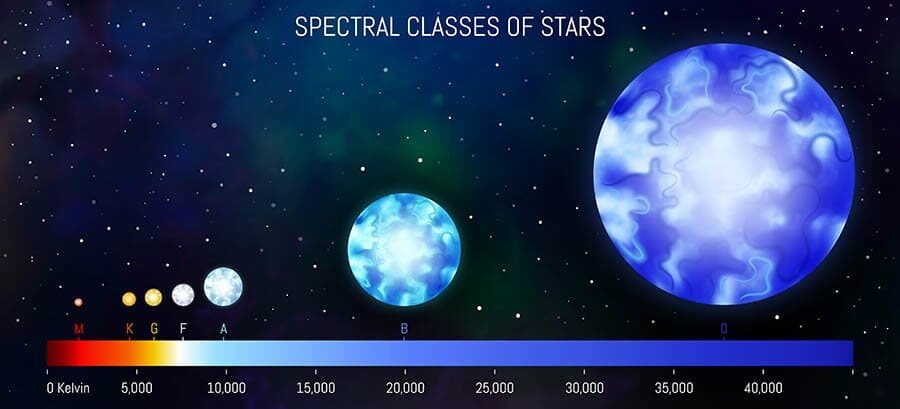
Harvard Spectral Classification
| Class | Temperature | Color |
|---|---|---|
| O | >28,000K | Blue, Violet |
| B | 10-28,000K | Blue |
| A | 7,500-10,000K | Blue |
| F | 6,000-7,500K | Blue, White |
| G | 5,000-6,000 | White, Yellow |
| K | 3,500-5,000K | Orange, Red |
| M | <3,500K | Red |
MK Spectral Classification
| Class | Name |
|---|---|
| 0/Ia+ | Hypergiant |
| Ia | very luminous supergiant |
| Iab | medium sized supergiant |
| Ib | less luminous supergiant |
| II | bright giant |
| III | normal giant |
| IV | subgiant |
| V | main sequence |
| VI | subdwarf |
| VII | white dwarf |
As well as dividing stars into their classification, we also divide them by their population too. we split this into first population, second population and third population.
- First Population – First population stars are the youngest in the galaxy. We classify the Sun as a first population star.
- Second Population – These are stars with little amounts of metal in them. Clusters usually have a lot of population two stars in them. They are older than first population stars.
- Third Population – These are the stars that have been around since the beginning, but at present they are only hypothetical.
More Facts about Stars
- Many stars out there in the universe are in a group of stars, and form part of a system. This can be a binary, which is two, or even more than this.
- When we look at stars, we are looking at them as they used to be in the past. If a star is 1 light year away, then we are looking at how this star looked a year ago.
- The bigger the star, the shorter it’s lifespan. A small star may live billions of years, whereas a massive star may only live 20 million years.
- The brightest star in the Earth’s night sky is known as Sirius A, which is Greek for “glowing”.
- The closest star to Earth (excluding the Sun) is Alpha Centauri, which is just over 4 light years away.
- Stars are essentially made from lots of dust and gas, which collapse due to gravity and form stars.
- When a group of stars are connected together to form a certain pattern, we call this a constellation.
- The oldest star charts that we have date back thousands of years to the Egyptians and the Babylonians.
- When we’re looking at the sky, all of these stars are bigger and brighter than our Sun – they have to be for us to be able to see them!
Most Common Questions about Stars
Why are stars different colors?
There are many different colors of stars out there, and this is generally related to how hot the star is. For example, a blue-white star is going to be hot, whilst a red star is going to be less hot. However, this isn’t the only thing that affects the color of a star. You also have to consider the material and composition of the star, as different elements may have an effect on it’s color.
Do stars move?
Yes, stars do move, but they are far enough away that you would never notice their movement, as it would take too long for it to get from another solar system to Earth. If you’re seeing the stars moving in the sky, this is because the Earth itself is moving. Remember that the Earth rotates once fully every 24 hours. So over time, it will look like the stars are moving.
Can stars be cold?
This really depends on your definition of the word star. If we take NASA’s definition of a star; “a sphere of gas held together by its own gravity”, then none of the stars that we look at in our night sky are actually cold, and they couldn’t be. They’re made up of hydrogen and helium, and even the smallest stars in the sky have a 1000°c or higher temperature. So no, what most of us know a star to be couldn’t be cold. However, we do have “brown dwarfs” in the universe, which can be referred to as stars, but they’re really not large enough to be defined as a star.
Are stars made up of gas?
Yes, stars are made up of a combination of hydrogen and helium. This is the same as our Sun, and it’s the same as the gas planets too. Stars can also be made up of lots of different elements like iron and carbon too, which can have an effect on the stars color.
Why are stars called stars?
The word star actually comes from the old English word Steorra. This is likely taken from the Latin word Stella, which means star.
The Sum Up
Hopefully, this has allowed you to understand the stars a little better than previously. The two different star systems can be a little confusing at first, but once you get used to them, you will be able to understand just how bright a star is by it’s stellar classification. If you have any more facts about stars, then please feel free to leave a comment below!